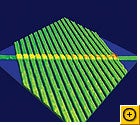
The Next Big thing? The memristor, a microscopic component that can "remember" electrical states even when turned off. It's expected to be far cheaper and faster than flash storage. A theoretical concept since 1971, it has now been built in labs and is already starting to revolutionize everything we know about computing, possibly making flash memory, RAM, and even hard drives obsolete within a decade.
The memristor is just one of the incredible technological advances sending shock waves through the world of computing. Other innovations in the works are more down-to-earth, but they also carry watershed significance. From the technologies that finally make paperless offices a reality to those that deliver wireless power, these advances should make your humble PC a far different beast come the turn of the decade.
In the following sections, we outline the basics of 15 upcoming technologies, with predictions on what may come of them. Some are breathing down our necks; some advances are still just out of reach. And all have to be reckoned with.
Memristor: A Groundbreaking New Circuit
32-Core CPUs From Intel and AMD
Nehalem and Swift Chips Spell the End of Stand-Alone Graphics Boards
USB 3.0 Speeds Up Performance on External Devices
Wireless Power Transmission
64-Bit Computing Allows for More RAM
Windows 7: It's Inevitable
Google's Desktop OS
Gesture-Based Remote Control
Radical Simplification Hits the TV Business
Curtains for DRM
Use Any Phone on Any Wireless Network
Your Fingers Do Even More Walking
Cell Phones Are the New Paper
Where You At? Ask Your Phone, Not Your Friend
25 Years of Predictions
The Future of Your PC's Hardware
Memristor: A Groundbreaking New Circuit
What is it? As its name implies, the memristor can "remember" how much current has passed through it. And by alternating the amount of current that passes through it, a memristor can also become a one-element circuit component with unique properties. Most notably, it can save its electronic state even when the current is turned off, making it a great candidate to replace today's flash memory.
Memristors will theoretically be cheaper and far faster than flash memory, and allow far greater memory densities. They could also replace RAM chips as we know them, so that, after you turn off your computer, it will remember exactly what it was doing when you turn it back on, and return to work instantly. This lowering of cost and consolidating of components may lead to affordable, solid-state computers that fit in your pocket and run many times faster than today's PCs.
Someday the memristor could spawn a whole new type of computer, thanks to its ability to remember a range of electrical states rather than the simplistic "on" and "off" states that today's digital processors recognize. By working with a dynamic range of data states in an analog mode, memristor-based computers could be capable of far more complex tasks than just shuttling ones and zeroes around.
When is it coming? Researchers say that no real barrier prevents implementing the memristor in circuitry immediately. But it's up to the business side to push products through to commercial reality. Memristors made to replace flash memory (at a lower cost and lower power consumption) will likely appear first; HP's goal is to offer them by 2012. Beyond that, memristors will likely replace both DRAM and hard disks in the 2014-to-2016 time frame. As for memristor-based analog computers, that step may take 20-plus years.
32-Core CPUs From Intel and AMD
What is it? With the gigahertz race largely abandoned, both AMD and Intel are trying to pack more cores onto a die in order to continue to improve processing power and aid with multitasking operations. Miniaturizing chips further will be key to fitting these cores and other components into a limited space. Intel will roll out 32-nanometer processors (down from today's 45nm chips) in 2009.
When is it coming? Intel has been very good about sticking to its road map. A six-core CPU based on the Itanium design should be out imminently, when Intel then shifts focus to a brand-new architecture called Nehalem, to be marketed as Core i7. Core i7 will feature up to eight cores, with eight-core systems available in 2009 or 2010. (And an eight-core AMD project called Montreal is reportedly on tap for 2009.)
After that, the timeline gets fuzzy. Intel reportedly canceled a 32-core project called Keifer, slated for 2010, possibly because of its complexity (the company won't confirm this, though). That many cores requires a new way of dealing with memory; apparently you can't have 32 brains pulling out of one central pool of RAM. But we still expect cores to proliferate when the kinks are ironed out: 16 cores by 2011 or 2012 is plausible (when transistors are predicted to drop again in size to 22nm), with 32 cores by 2013 or 2014 easily within reach. Intel says "hundreds" of cores may come even farther down the line.
Nehalem and Swift Chips Spell the End of Stand-Alone Graphics Boards
When AMD purchased graphics card maker ATI, most industry observers assumed that the combined company would start working on a CPU-GPU fusion. That work is further along than you may think.
What is it? While GPUs get tons of attention, discrete graphics boards are a comparative rarity among PC owners, as 75 percent of laptop users stick with good old integrated graphics, according to Mercury Research. Among the reasons: the extra cost of a discrete graphics card, the hassle of installing one, and its drain on the battery. Putting graphics functions right on the CPU eliminates all three issues.
Chip makers expect the performance of such on-die GPUs to fall somewhere between that of today's integrated graphics and stand-alone graphics boards--but eventually, experts believe, their performance could catch up and make discrete graphics obsolete. One potential idea is to devote, say, 4 cores in a 16-core CPU to graphics processing, which could make for blistering gaming experiences.
When is it coming? Intel's soon-to-come Nehalem chip includes graphics processing within the chip package, but off of the actual CPU die. AMD's Swift (aka the Shrike platform), the first product in its Fusion line, reportedly takes the same design approach, and is also currently on tap for 2009.
Putting the GPU directly on the same die as the CPU presents challenges--heat being a major one--but that doesn't mean those issues won't be worked out. Intel's two Nehalem follow-ups, Auburndale and Havendale, both slated for late 2009, may be the first chips to put a GPU and a CPU on one die, but the company isn't saying yet.
USB 3.0 Speeds Up Performance on External Devices
The USB connector has been one of the greatest success stories in the history of computing, with more than 2 billion USB-connected devices sold to date. But in an age of terabyte hard drives, the once-cool throughput of 480 megabits per second that a USB 2.0 device can realistically provide just doesn't cut it any longer.
What is it? USB 3.0 (aka "SuperSpeed USB") promises to increase performance by a factor of 10, pushing the theoretical maximum throughput of the connector all the way up to 4.8 gigabits per second, or processing roughly the equivalent of an entire CD-R disc every second. USB 3.0 devices will use a slightly different connector, but USB 3.0 ports are expected to be backward-compatible with current USB plugs, and vice versa. USB 3.0 should also greatly enhance the power efficiency of USB devices, while increasing the juice (nearly one full amp, up from 0.1 amps) available to them. That means faster charging times for your iPod--and probably even more bizarre USB-connected gear like the toy rocket launchers and beverage coolers that have been festooning people's desks.
When is it coming? The USB 3.0 spec is nearly finished, with consumer gear now predicted to come in 2010. Meanwhile, a host of competing high-speed plugs--DisplayPort, eSATA, and HDMI--will soon become commonplace on PCs, driven largely by the onset of high-def video. Even FireWire is looking at an imminent upgrade of up to 3.2 gbps performance. The port proliferation may make for a baffling landscape on the back of a new PC, but you will at least have plenty of high-performance options for hooking up peripherals.
Wireless Power Transmission
Wireless power transmission has been a dream since the days when Nikola Tesla imagined a world studded with enormous Tesla coils. But aside from advances in recharging electric toothbrushes, wireless power has so far failed to make significant inroads into consumer-level gear.
What is it? This summer, Intel researchers demonstrated a method--based on MIT research--for throwing electricity a distance of a few feet, without wires and without any dangers to bystanders (well, none that they know about yet). Intel calls the technology a "wireless resonant energy link," and it works by sending a specific, 10-MHz signal through a coil of wire; a similar, nearby coil of wire resonates in tune with the frequency, causing electrons to flow through that coil too. Though the design is primitive, it can light up a 60-watt bulb with 70 percent efficiency.
When is it coming? Numerous obstacles remain, the first of which is that the Intel project uses alternating current. To charge gadgets, we'd have to see a direct-current version, and the size of the apparatus would have to be considerably smaller. Numerous regulatory hurdles would likely have to be cleared in commercializing such a system, and it would have to be thoroughly vetted for safety concerns.
Assuming those all go reasonably well, such receiving circuitry could be integrated into the back of your laptop screen in roughly the next six to eight years. It would then be a simple matter for your local airport or even Starbucks to embed the companion power transmitters right into the walls so you can get a quick charge without ever opening up your laptop bag.
Reference : http://www.pcworld.com/article/152683/tech.html?tk=rss_news








No comments:
Post a Comment